Key Points
- When choosing a corn hybrid for silage, one needs to consider how the silage will be utilized - for either a feedlot, dairy or cow/calf operation.
- The following factors must be taken into consideration when selecting a corn hybrid for silage:
- Hybrid maturity, technology traits for insect resistance, agronomic stability, genetic resistance, proven yield potential, starch content, fibre and starch digestibility, and agronomic considerations.
Factors to consider when selecting a corn hybrid for silage:
Hybrid Maturity
- Pick an appropriate maturity to ensure quality and yield are met but that the product is ready in an appropriate harvest window.
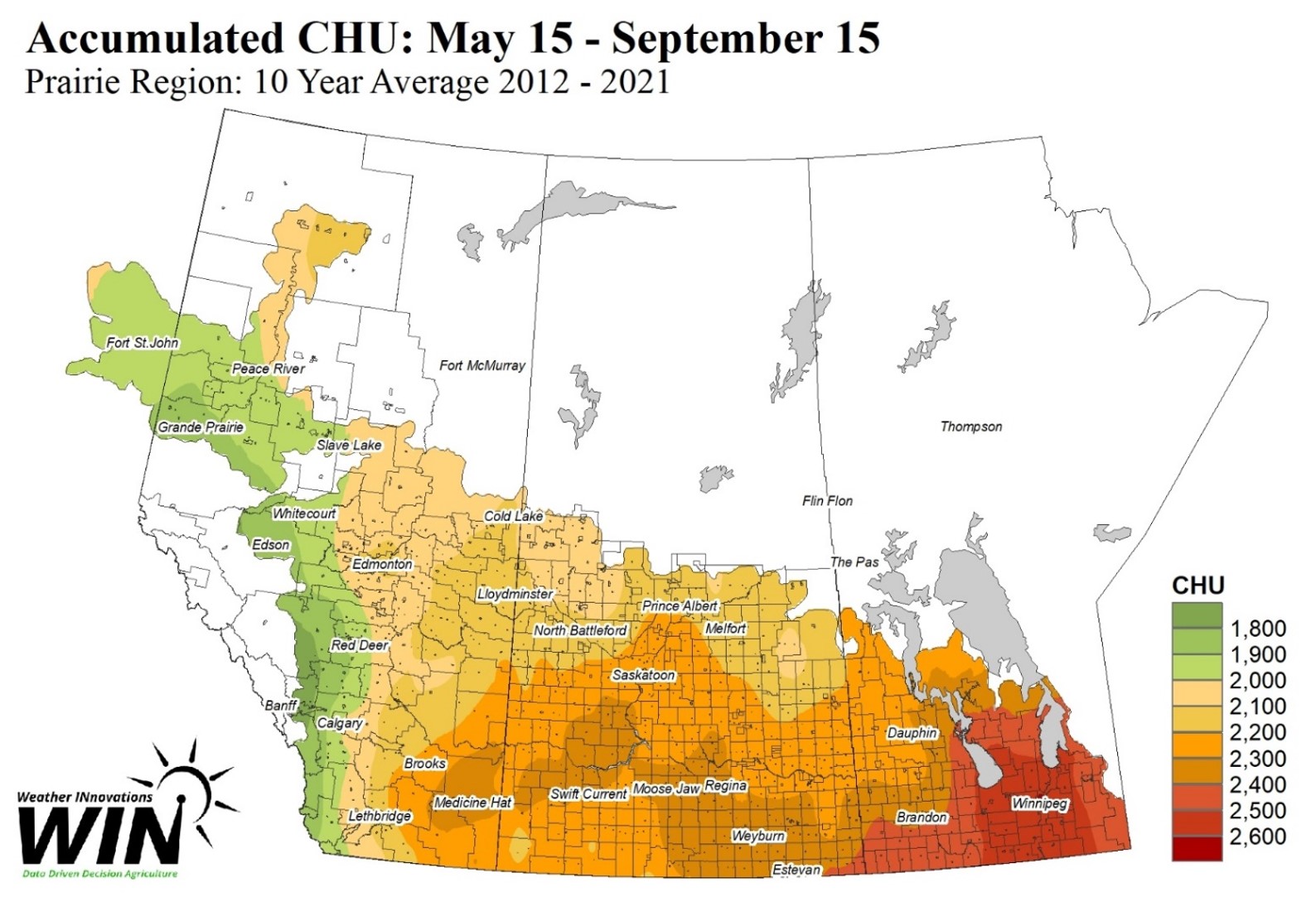
- In Canada, maturity is rated in terms of Corn Heat Units (CHU’s); i.e., 2100 CHU. CHU is a measure of cumulative heat over the growing season.
- It is recommended to select a silage hybrid that is 100-150 CHU longer than a hybrid grown for grain.
Technology Traits
- Look for hybrids with Insect resistant traits (Qrome®, Optimum® AcreMax®) and herbicide tolerance traits.
Agronomic Stability
- Stress emergence and drought tolerance, along with stalk and root strength are key attributes for improved standability.
Genetic Resistance
- Genetic resistance to diseases such as Goss’ wilt.
Proven Yield Potential
- Biomass yield – influenced by plant height and maturity of the ear.
- Starch yield – influenced by grain yield of the ear.
- Silage tonnage (dry matter yield) is primarily a function of:
- Silage harvest timing – important because grain (starch) contributes about half of the dry matter yield (and a significant portion of the energy ~65%)
Hybrid genetics

Starch Content
- Primarily driven by genetics and environment.
- Highest energy component of the corn plant is the kernel.
- Heavily influenced by harvest maturity of the kernel.
- Short statured plants generally have high starch energy but may lack overall plant biomass and tonnage.
- Grain to stover ratio is the biggest factor affecting the energy value of corn silage.
- Generally, the grain to stover ratio (G:S) is 30:70 to 50:50 on a dry matter basis.
Fibre and Starch Digestibility
- Starch digestibility is the amount of starch digested in the rumen and the intestines.
- Starch digestibility is influenced by kernel maturity and the extent of kernel processing. It is optimized 60-90 days post ensiling.
- Fibre digestibility is influenced 3 times more by growing conditions than genetics.
- Fibre digestibility between different hybrids is generally the same when measured at 35% dry matter.
Agronomic Considerations
- Pioneer ® brand corn offers a range of both insect protection traits and proven effective seed treatments to combat both insect pests and damaging diseases that affect corn plants.
- Qrome® - provides above and below ground insect protection (European Corn Borer and Corn Rootworm).
- Optimum® AcreMax® - European Corn Borer
- In addition to broad spectrum standard fungicide seed treatments, Pioneer ® brand corn offers Lumivia® insecticide seed treatment which provides enhanced early season protection against yield robbing insects such as wireworm and cutworms.
Corn Silage Summary
- Corn silage yield and quality are determined by the interaction of:
G x E x M (Genetics, Environment, Management)
- Silage yield is primarily driven by biomass (plant height at the ear) and starch content.
- Starch (grain) typically contributes half of silage dry matter yield.
- Silage yield is influenced by harvest timing, seed genetics and planting date in addition to weather, soil, and fertility.
- Feed quality is primarily driven by starch
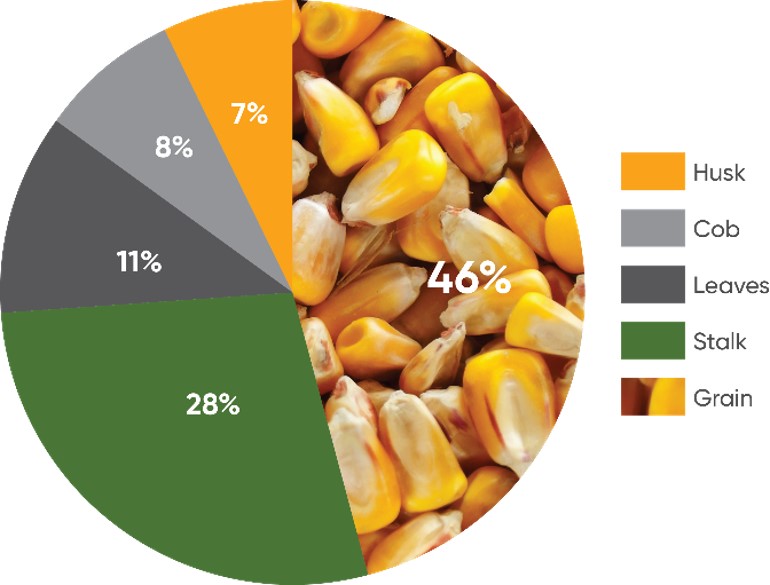
Figure 1. Silage yield components. Source: Mahanna et al., 2018. Silage Zone Manual, Third Edition.