Something went wrong. Please try again later...
Key Points
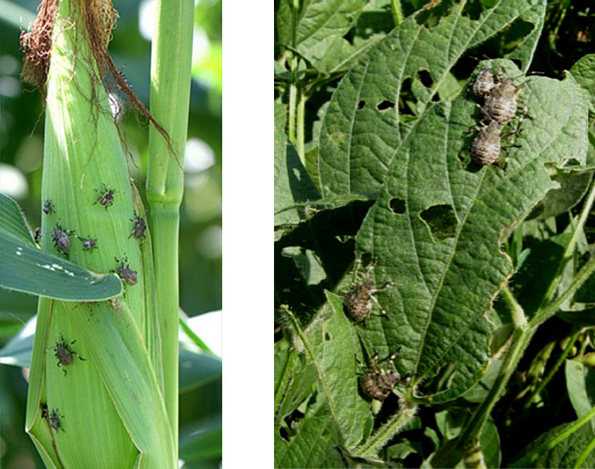
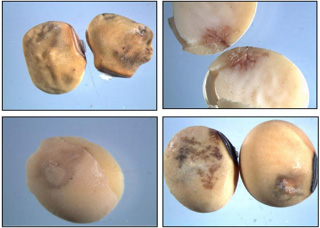
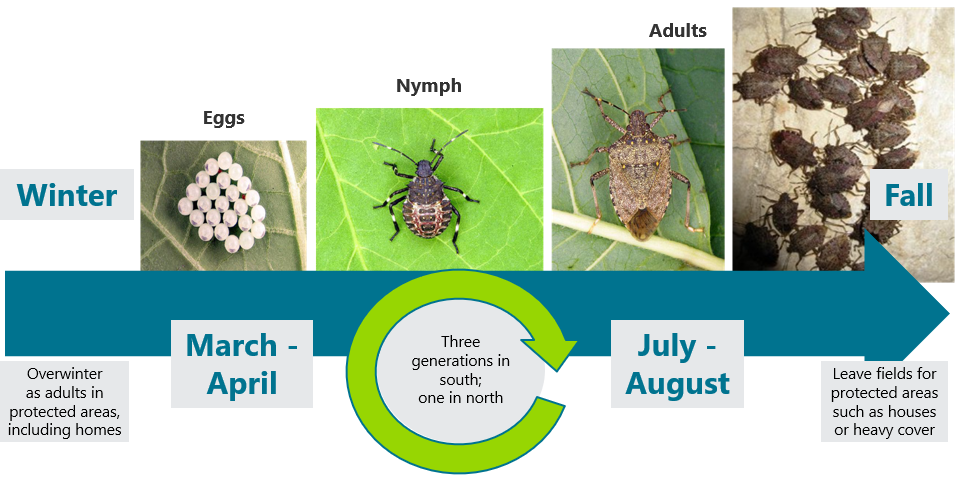
- Brown marmorated stink bug is an invasive species that is a serious pest of numerous fruit, vegetable, and field crops.
- BMSB feeding can impact grain quality by causing damage to soybean seeds and corn ears.
The foregoing is provided for informational use only. Please contact your Pioneer sales professional for information and suggestions specific to your operation. Product performance is variable and depends on many factors such as moisture and heat stress, soil type, management practices and environmental stress as well as disease and pest pressures. Individual results may vary. Pioneer® brand products are provided subject to the terms and conditions of purchase which are part of the labeling and purchase documents.