6/27/2025
Corn Foliar Fungicide Modes of Action

Crop Focus
Written by Mark Jeschke, Ph.D., Pioneer Agronomy Manager
Key Points
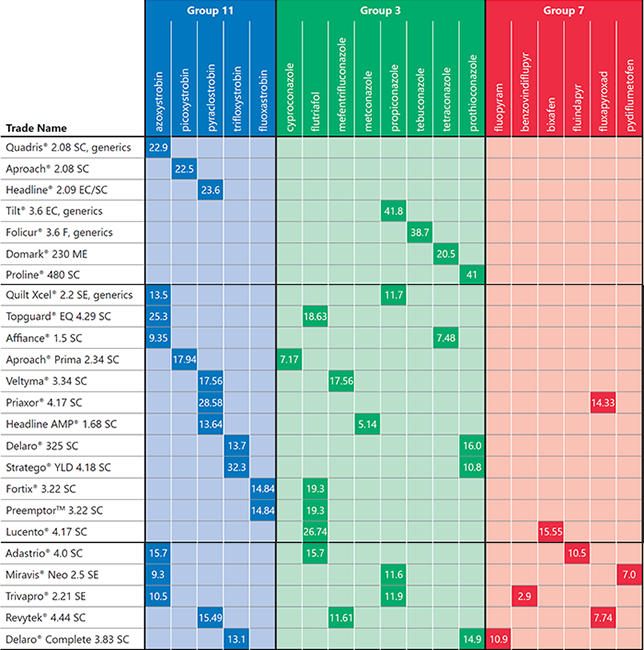
- Many newer foliar fungicide products for corn have 2 or 3 active ingredients with different target sites.
- Target site is the basis for FRAC codes, which are group numbers assigned by the Fungicide Resistance Action Committee that are shown on fungicide product labels. In practice, the term “mode of action” is often used interchangeably with target site or FRAC group.
- Fungicides with multiple modes of action can provide more effective disease control and reduce selection for resistance in pathogens.
The foregoing is provided for informational use only. Contact your Pioneer sales professional for information and suggestions specific to your operation. Product performance is variable and subject to any number of environmental, disease, and pest pressures. Individual results may vary. Pioneer® brand products are provided subject to the terms and conditions of purchase which are part of the labeling and purchase documents.